Nutritional Composition of 100g Blueberries: Blueberry Nutrition Facts 100g

Blueberry nutrition facts 100g – Blueberries are a nutritional powerhouse, packing a significant punch of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants into their small size. Understanding their nutritional composition can help us appreciate their role in a healthy diet. This section details the macronutrient and micronutrient profile of a 100g serving of these delicious berries.
Macronutrient Breakdown of 100g Blueberries
The macronutrients – carbohydrates, proteins, and fats – provide the body with energy. Blueberries are primarily a source of carbohydrates, with a smaller contribution from protein and a negligible amount of fat. The following table provides a detailed breakdown:
| Nutrient | Amount (grams) | Amount (% Daily Value) | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 14.5 | 5 | g |
| Protein | 0.7 | 1 | g |
| Fat | 0.3 | 0 | g |
Note
Daily Value percentages are approximate and may vary based on individual caloric needs.*
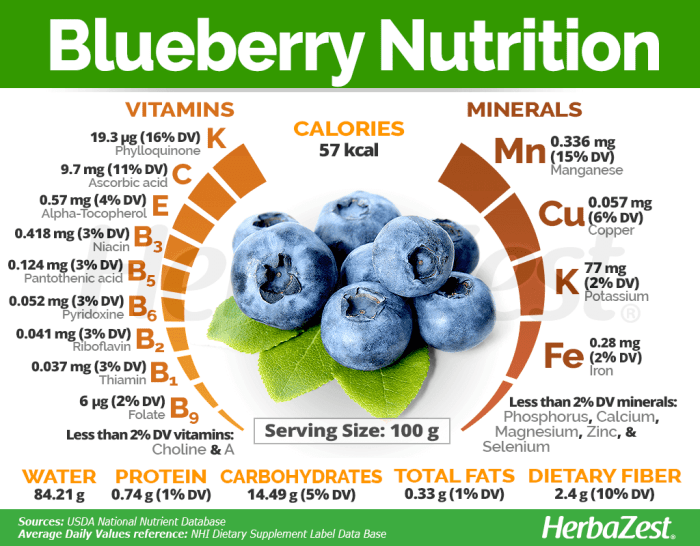
Micronutrient Content of 100g Blueberries
Beyond macronutrients, blueberries are rich in various micronutrients vital for numerous bodily functions. These include:
- Vitamin C: A potent antioxidant, crucial for immune function and collagen synthesis. A 100g serving provides a significant portion of the recommended daily intake.
- Vitamin K: Essential for blood clotting and bone health. Blueberries contribute to the daily requirement of this important vitamin.
- Vitamin A (as beta-carotene): A precursor to Vitamin A, vital for vision and cell growth. Blueberries offer a modest amount.
- Manganese: A mineral involved in bone health, wound healing, and metabolism. Blueberries are a good source.
- Potassium: An electrolyte essential for maintaining fluid balance and blood pressure. A 100g serving contributes to the daily potassium needs.
Fiber Content of 100g Blueberries
Dietary fiber is crucial for digestive health and overall well-being. Blueberries are a good source of both soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels and cholesterol, while insoluble fiber promotes regular bowel movements. A 100g serving of blueberries contains approximately 2.4 grams of fiber, a combination of both soluble and insoluble types. The exact ratio of soluble to insoluble fiber can vary slightly depending on factors such as growing conditions and ripeness.
Visual Representation of Blueberry Nutrition

Understanding the nutritional profile of blueberries is easier when visualized. The following text-based representations aim to illustrate the macronutrient and micronutrient composition of a 100g serving. These are simplified representations for clarity and understanding.
Macronutrient Composition of Blueberries
To visualize the macronutrient breakdown in 100g of blueberries, imagine a pie chart. The largest slice would represent carbohydrates, occupying roughly 85% of the chart, reflecting the substantial carbohydrate content of blueberries. A smaller slice, approximately 10%, would represent water, highlighting the high water content in this fruit. The remaining small slice, about 5%, would represent a combination of protein and fats, indicating their relatively minor contribution to the overall macronutrient profile.
Understanding blueberry nutrition facts per 100g is crucial for balanced eating. While blueberries offer fantastic antioxidant benefits, it’s also helpful to compare their nutritional profile to other foods, such as checking out the details on cheese slice nutrition facts to understand the contrasting macronutrient compositions. Returning to blueberries, their relatively low calorie count and high fiber content make them a popular choice for health-conscious individuals.
This is a simplified representation, and the exact proportions may vary slightly depending on the specific type and growing conditions of the blueberries.
Micronutrient Composition of Blueberries, Blueberry nutrition facts 100g
Consider a bar chart to represent the key vitamins and minerals found in 100g of blueberries. The bars would vary in height, reflecting the differing concentrations of each nutrient. Vitamin C would have a tall bar, showing its significant presence. Similarly, manganese would have a noticeably tall bar, indicating its high concentration. Other vitamins and minerals like vitamin K, vitamin E, and potassium would have moderately sized bars, reflecting their presence in moderate amounts.
Finally, several other vitamins and minerals like fiber, vitamin B6, copper, and others would be represented by smaller bars, reflecting their lower concentrations compared to the aforementioned nutrients. This visualization emphasizes the abundance of specific vitamins and minerals within this small but nutritionally dense fruit.
Considerations for Blueberry Consumption
While blueberries offer a wealth of nutritional benefits, it’s important to consider certain aspects of their consumption to maximize their positive impact on health and well-being. Understanding potential drawbacks, proper storage techniques, and the possibility of allergic reactions ensures safe and effective enjoyment of these superfoods.
Potential Drawbacks of High Blueberry Consumption
Consuming extremely large quantities of blueberries might lead to some minor digestive issues, such as diarrhea or stomach upset, due to their high fiber content. This is generally not a serious concern unless exceptionally high amounts are consumed. Furthermore, individuals on blood thinners should consult their physician before significantly increasing their blueberry intake, as the high vitamin K content could potentially interact with these medications.
Finally, while rare, phytic acid present in blueberries can interfere with the absorption of certain minerals. However, this effect is generally minimal, especially when blueberries are consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Selecting and Storing Blueberries to Preserve Nutritional Value
Choosing and storing blueberries correctly is crucial for maintaining their nutritional integrity and flavor. Look for firm, plump blueberries with a deep blue color and a dry surface. Avoid berries that are soft, mushy, or have blemishes. Upon purchasing, gently rinse the blueberries under cold water before storing them. Refrigeration is ideal; store them in a shallow container, ideally lined with a paper towel to absorb excess moisture, in the refrigerator for up to a week.
Freezing is also a viable option for longer-term storage; spread the berries on a baking sheet before freezing to prevent clumping, then transfer them to a freezer-safe bag or container. Proper storage methods help to prevent spoilage and nutrient loss.
Blueberry Allergies and Identification
Allergic reactions to blueberries are relatively uncommon but can occur. Symptoms can range from mild, such as itching or hives around the mouth, to more severe reactions, including swelling of the throat or difficulty breathing (anaphylaxis). These reactions are typically caused by proteins found within the berry. If you suspect a blueberry allergy, it’s crucial to discontinue consumption immediately and seek medical attention if symptoms are severe.
A proper diagnosis can be made through allergy testing performed by a medical professional. Individuals with known allergies to other berries or pollen might have a higher risk of developing a blueberry allergy. Careful observation of any reactions after consuming blueberries is important, particularly for individuals with a family history of allergies.
FAQ Corner
Are blueberries good for weight loss?
Blueberries are relatively low in calories and high in fiber, which can contribute to feelings of fullness and aid in weight management. However, they should be part of a balanced diet and exercise plan for optimal weight loss results.
Can I freeze blueberries to preserve their nutrients?
Yes, freezing blueberries is an excellent way to preserve their nutritional value. Freezing quickly after harvesting helps retain most vitamins and antioxidants.
Do blueberries interact with any medications?
While generally safe, blueberries’ high vitamin K content might affect individuals on blood-thinning medications. Consult your doctor if you have concerns.
What are the best ways to incorporate blueberries into my diet?
Blueberries are versatile! Enjoy them fresh, in smoothies, yogurt, oatmeal, baked goods, or as a topping for salads and desserts.
Are there any potential side effects from eating too many blueberries?
While rare, consuming excessive amounts might lead to digestive upset due to the high fiber content. Moderation is key.
